[ad_1]
Getting things done on a Mac with a weak WiFi signal is difficult at best and impossible at worst.
Sure, not all apps require an internet connection to work, but even something as simple as writing a short document can be cumbersome when you can’t look up information online, access your cloud-based calendar, and email the document to its intended recipient.
The good news is there are multiple ways how to improve WiFi signal without leaving your current internet service provider. Let’s explore the most effective techniques so you can say goodbye to abysmal download and upload speeds, high latency, and annoying connection drops.
10 Tried-and-Tested Ways to Improve WiFi
The quality of a WiFi signal can be improved in a number of different ways. Some ways take no time and money to try, while others require a substantially larger investment.
The most cost-effective approach then is to start with low-effort methods and gradually move on to those that require more effort.
1. Test Your WiFi Speed
While testing your WiFi speed won’t improve your WiFi signal on its own, it accomplishes two very important things:
- Provides you with a reference point that you can use for comparison purposes.
- Tells you if you’re able to achieve the speed advertised by your internet service provider.
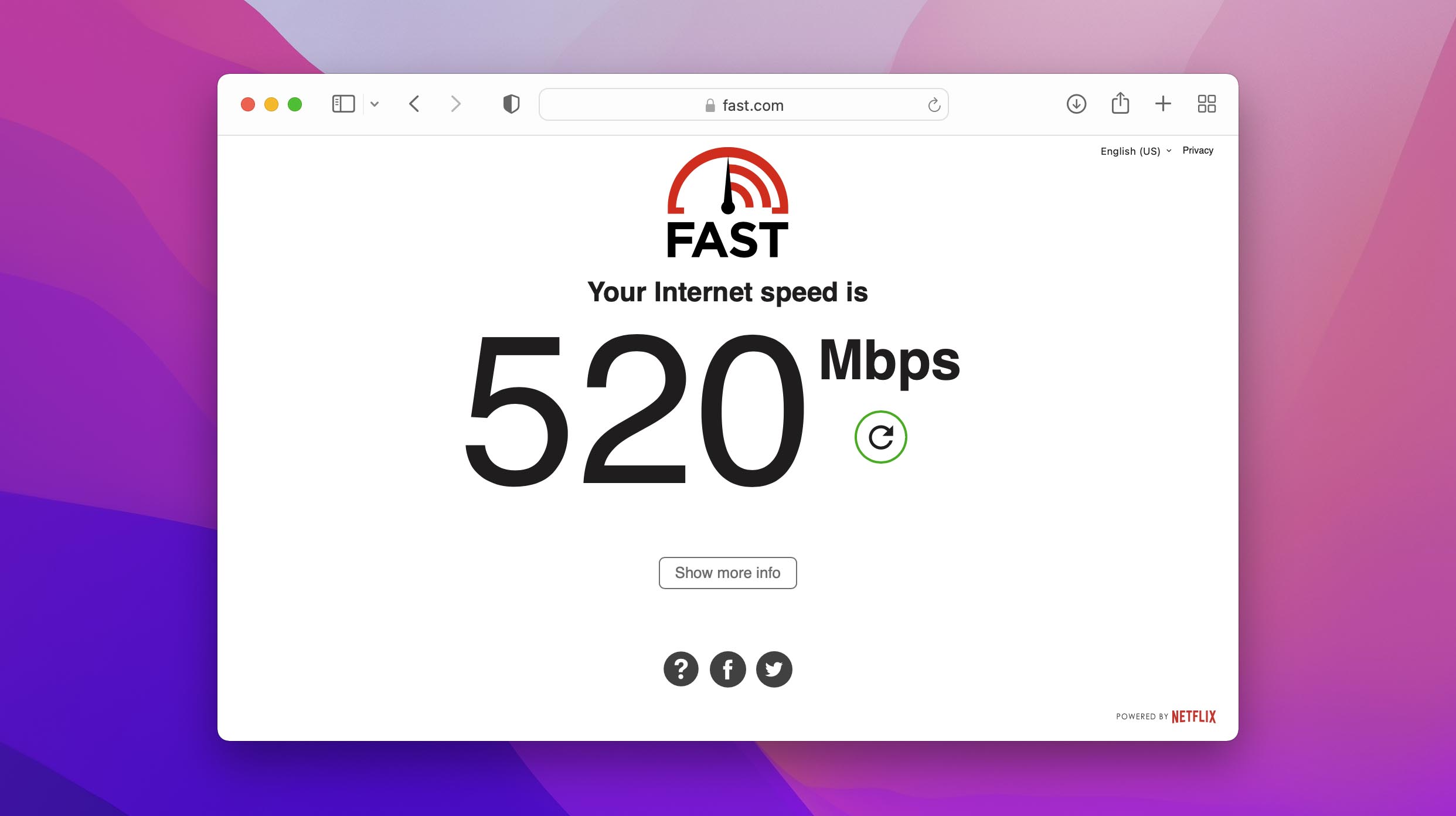
If you discover that you’re way short of the WiFi speeds you should be getting, you might want to consider contacting your internet service provider right away—especially if you have no reason to believe that something is wrong on your side.
2. Restart Your WiFi Router
As Moss and Roy from The IT Crowd always say, “Have you tried turning it off and on again?” While this piece of advice may seem somewhat condescending, the fact is that a simple router restart can solve many issues and, ultimately, improve your WiFi signal.
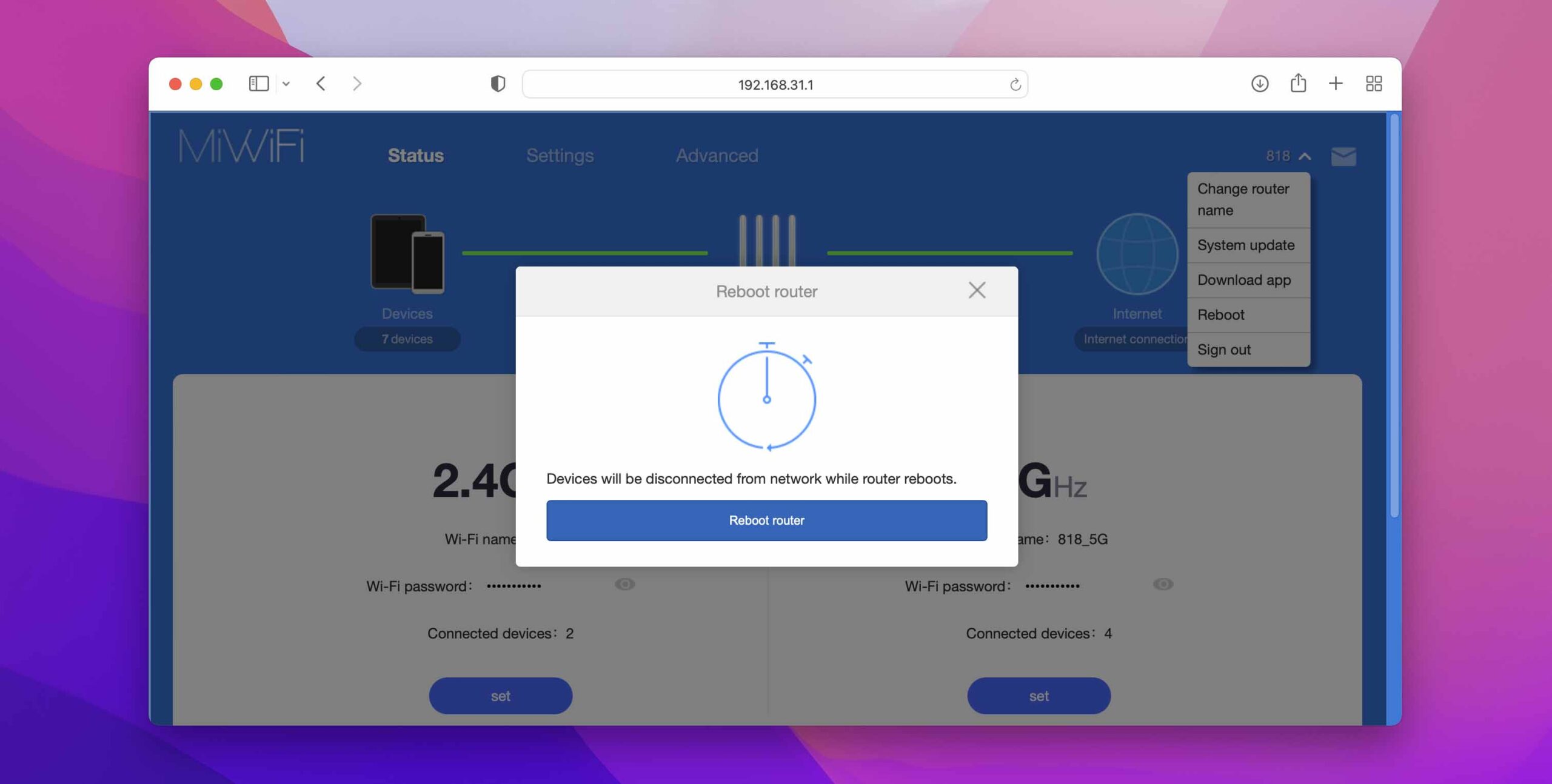
Restarting helps because modern routers are basically small computers, and they store a lot of information in temporary storage locations called caches. For example, your router maintains a cache with DNS records, which provide information on how to handle requests for domain names.
Over time, this information can become corrupted, and a simple restart is enough to clear the entire cache and force the router to recreate it from scratch.
3. Check Your Network Diagnostics
Your Mac can detect common problems with your wireless connection, and you don’t even need to install a third-party tool thanks to the built-in Wireless Diagnostics utility. To access it:
- Hold the Option key and click the WiFi icon in the menu bar.
- Click the Wireless Diagnostics options.
- A window with an introduction to the Wireless Diagnostics tool will appear. Read the instructions and click Continue to begin diagnosing your wireless environment and configuration.
- Wait until Wireless Diagnostics finishes running all tests.
- Apply the recommended fixes or, if no issues are detected, monitor your WiFi connection for problems.
Keep in mind that the results of the Wireless Diagnostics process can be influenced by the location of your Mac, as well as the time when you perform the test.
4. Analyze Your WiFi Coverage
Location-dependent diagnostics tools like the Wireless Diagnostics utility can provide some information about your WiFi signal and its strength, but they don’t tell the full story because they don’t analyze WiFi coverage.
In other words, they don’t tell you how far can the signals broadcasted by your WiFi router reach before they become too weak to detect. That’s where WiFi site survey software apps like NetSpot WiFi analyzer come in.
With NetSpot, you can easily perform a WiFi site survey by collecting data samples from multiple locations. NetSpot will then analyze the collected data for you, and transform it into detailed heatmaps that reveal performance issues at a glance.
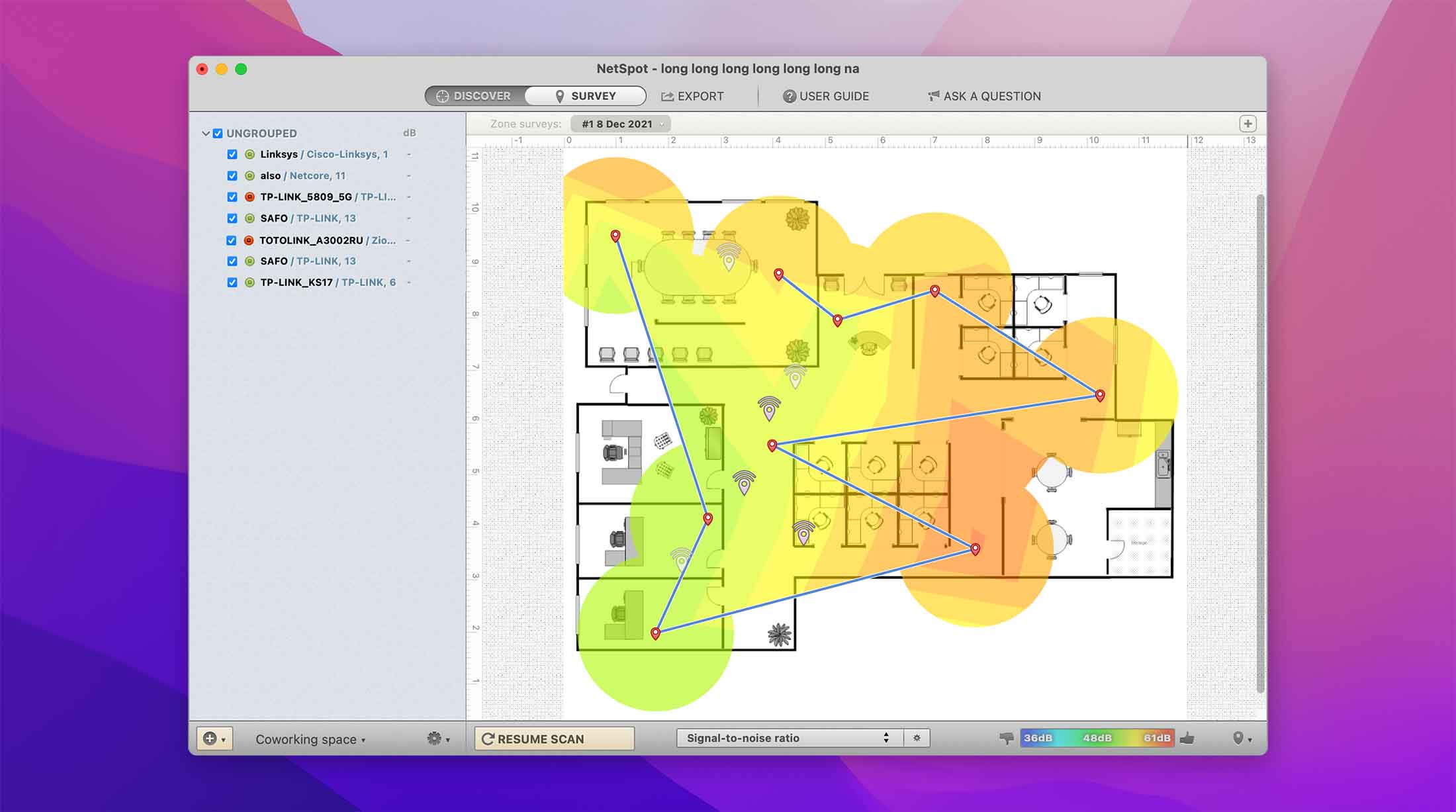
NetSpot can create over 15 heatmap visualizations to help you analyze everything from signal-to-noise ratio to frequency band coverage to wireless transmit rate, and you can download the app for free from its website.
5. Move Your Router
After performing a WiFi site survey using a WiFi analyzer like NetSpot, you should have a pretty good idea of how well placed your router is. If one part of the area you want to cover with a strong WiFi signal is covered flawlessly, but another part is riddled with signal dead zones, then it’s time to move the router to a better place.
Generally, the router should be located roughly in the middle of your living space. If that’s not possible, choose a location that’s obstructed the least. For example, an open-plan living room is guaranteed to block the signals broadcasted by the router less than a cramped kitchen full of large appliances emitting radio frequency noise.
You can always verify that the new location has improved WiFi coverage by performing another WiFi site survey using NetSpot or some other similar WiFi analyzer.
6. Prune Unnecessary Connections
You might be surprised by how many devices have access to your WiFi network. From smart appliances to your neighbors’ kids and their friends, every additional connection creates an extra load on your WiFi router. If the total load exceeds a certain threshold, everyone’s download and upload speeds suffer, which is why you should proactively prune unnecessary connections on a regular basis.
The easiest way to do that is to change the WiFi password. By doing so, you will force all connected devices to reconnect, which won’t be possible without the new password.
To change your WiFi password, you need to:
- Log in to your router’s admin interface.
- Go to wireless security settings.
- Enter the new password and wait for the WiFi interface or the entire router to restart.
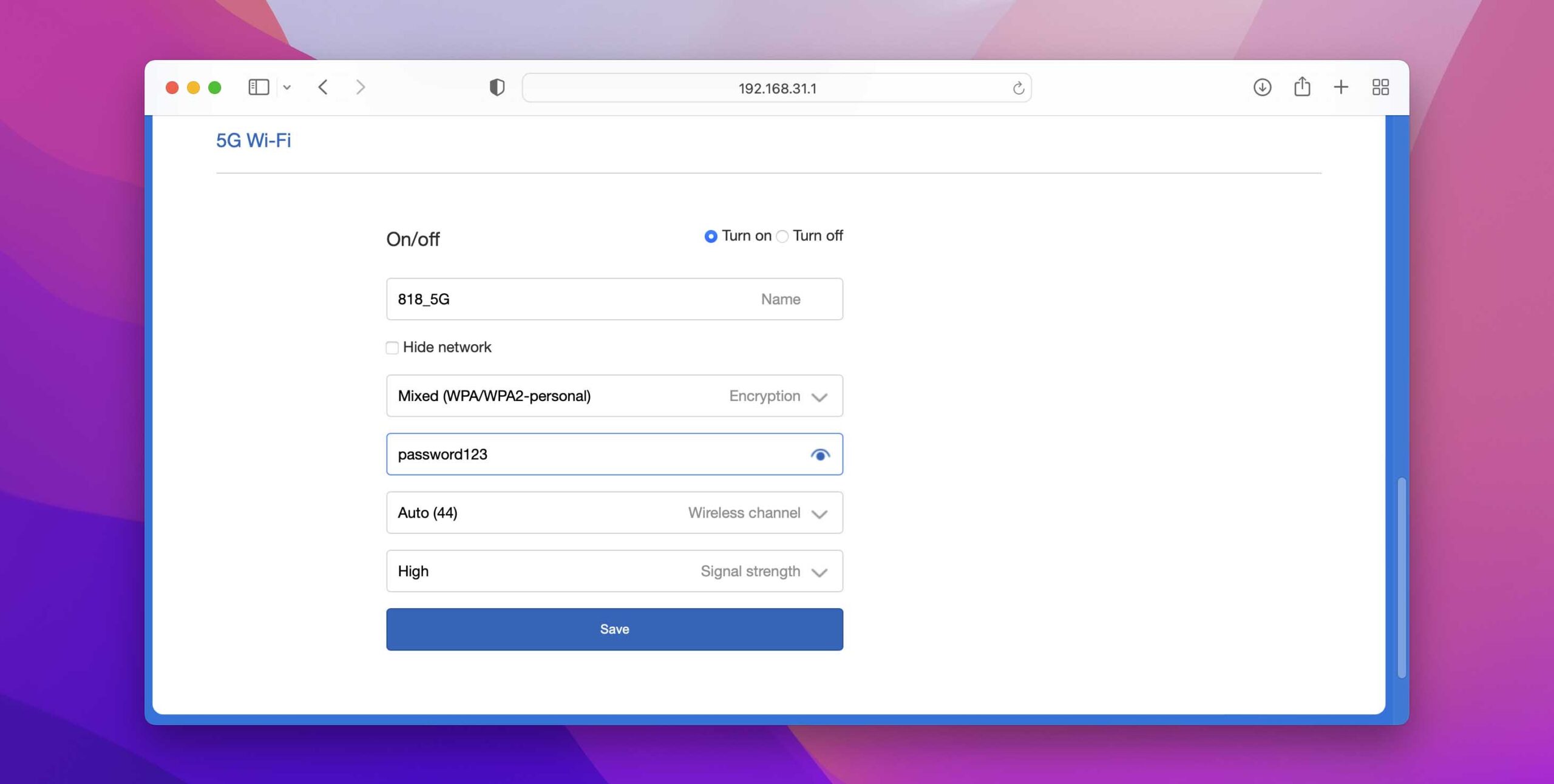
Using this method, you can improve your WiFi signal nearly instantly, and enjoy a faster and more stable connection to the internet for as long as you keep your password to yourself.
7. Change a WiFi Channel or Band
Your router broadcasts on a specific band and channel. A band is a distinct radio frequency range, and the two most commonly used bands—2.4 and 5 GHz—are both divided into multiple channels.
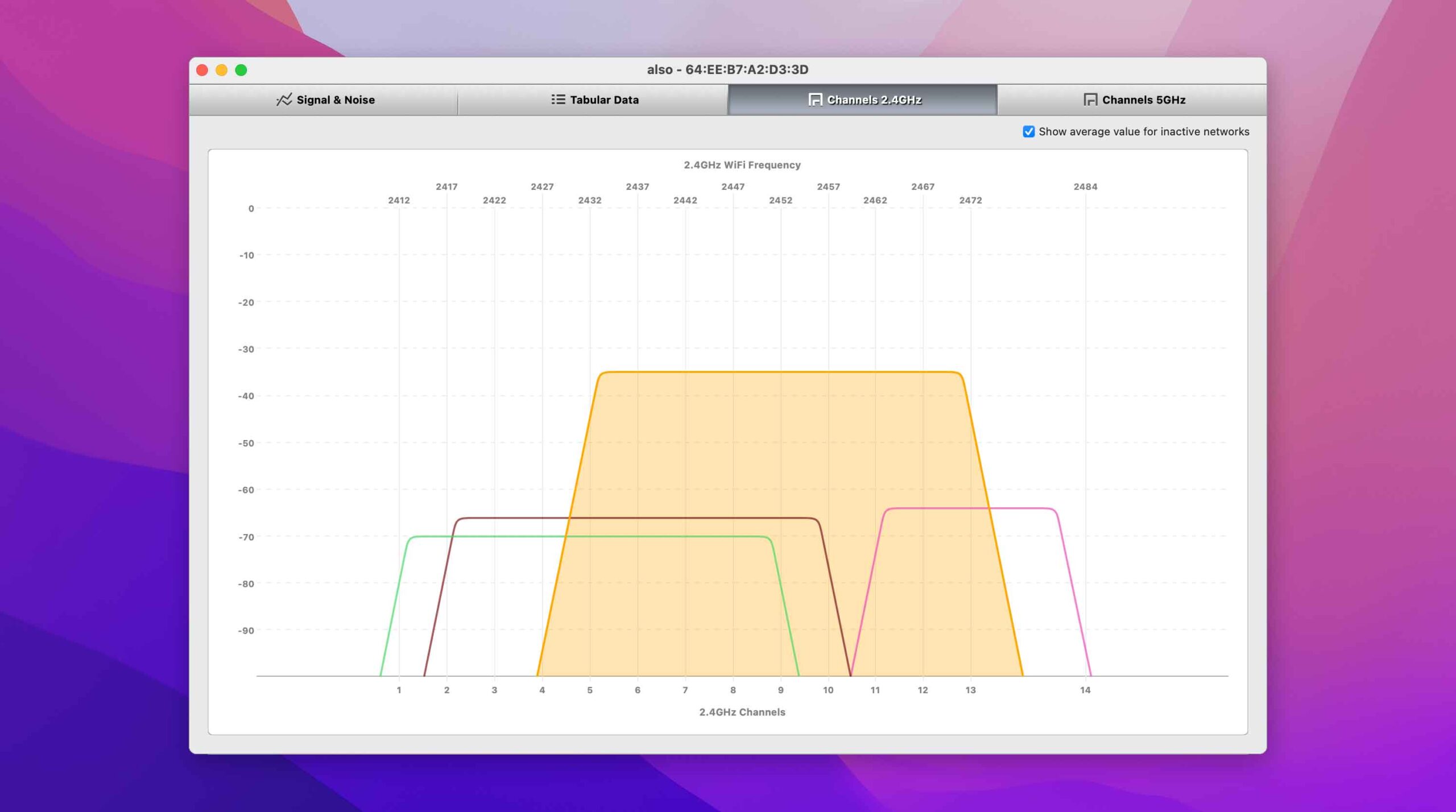
- The 2.4 GHz band is divided into 11 channels in North America, but only three of these channels (1, 6, and 11) are non-overlapping.
- The 5 GHz band is divided into dozens and dozens of channels, so overlapping or co-channel interference are rarely issues that need to be solved manually.
To decide which non-overlapping channel in the 2.4 GHz band is suitable the most, you need to find out how many individual channels are utilized and pick the one that’s utilized the least. A WiFi tool like NetSpot makes this easy to find the best WiFi channel and can do even more than that.
8. Upgrade Your Router’s Firmware
Your router is controlled by specialized software called firmware. Much like macOS, router firmware may contain all kinds of bugs and optimization issues, which may negatively affect its performance and expose it to dangerous malware.
Luckily, most modern routers update themselves automatically at regular intervals. To check if you’re using the latest firmware available:
- Log in to your router’s admin interface.
- Go to Advanced settings.
- Look for a Firmware update option (often located in the Administration section).
- Check if a new firmware version is available.
- If it is, install it.
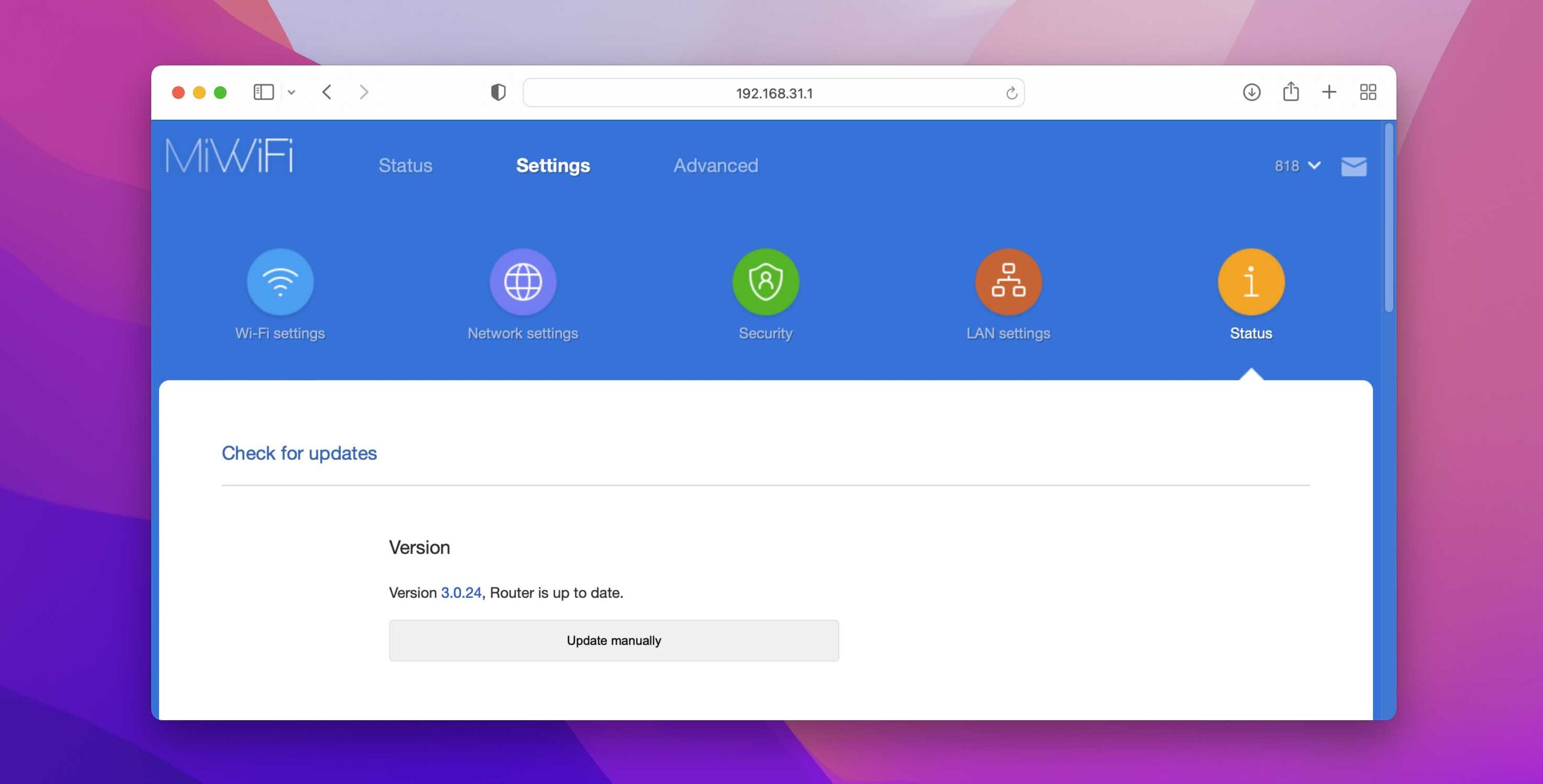
Keep in mind that all routers are different, so the update option may be located in a completely different part of your router’s admin interface, so consider the steps above as a mere illustration of the process.
9. Get a WiFi Extender
A WiFi extender is a handy little device that you can plug into any standard wall outlet to extend the reach of your existing WiFi network.

WiFi extenders can be very inexpensive, but the cheaper models typically create a separate WiFi network, forcing your devices to switch between networks when roaming around.
More expensive WiFi extenders can create a mesh WiFi network together with the main router to cover a large area with a single network.
10. Buy a New Router
Buying a new router is certainly the nuclear option when it comes to improving a WiFi signal on Mac, but it can be extremely effective.
Modern routers support all kinds of useful features, including multi-user, multiple-input, multiple-output technology—better known as MU-MIMO—beamforming, and others.
They also support the latest WiFi standards (Wi-Fi 6, for example), offering much greater throughput, especially in high-density scenarios.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are many effective ways to improve a WiFi signal and eliminate issues with poor download and upload speed, high latency, and insufficient signal strength. Regardless of which of the methods described in this article you decide to try, we highly recommend you always use a WiFi signal analyzer tool like NetSpot to check WiFi performance before and after so that you know if you’re getting closer to accomplishing your goal.